Inflammation is a natural process that occurs in the body as a response to injury or infection. It is an essential part of the immune system's defense mechanism and helps to protect the body from harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. However, chronic inflammation can have damaging effects on the body.
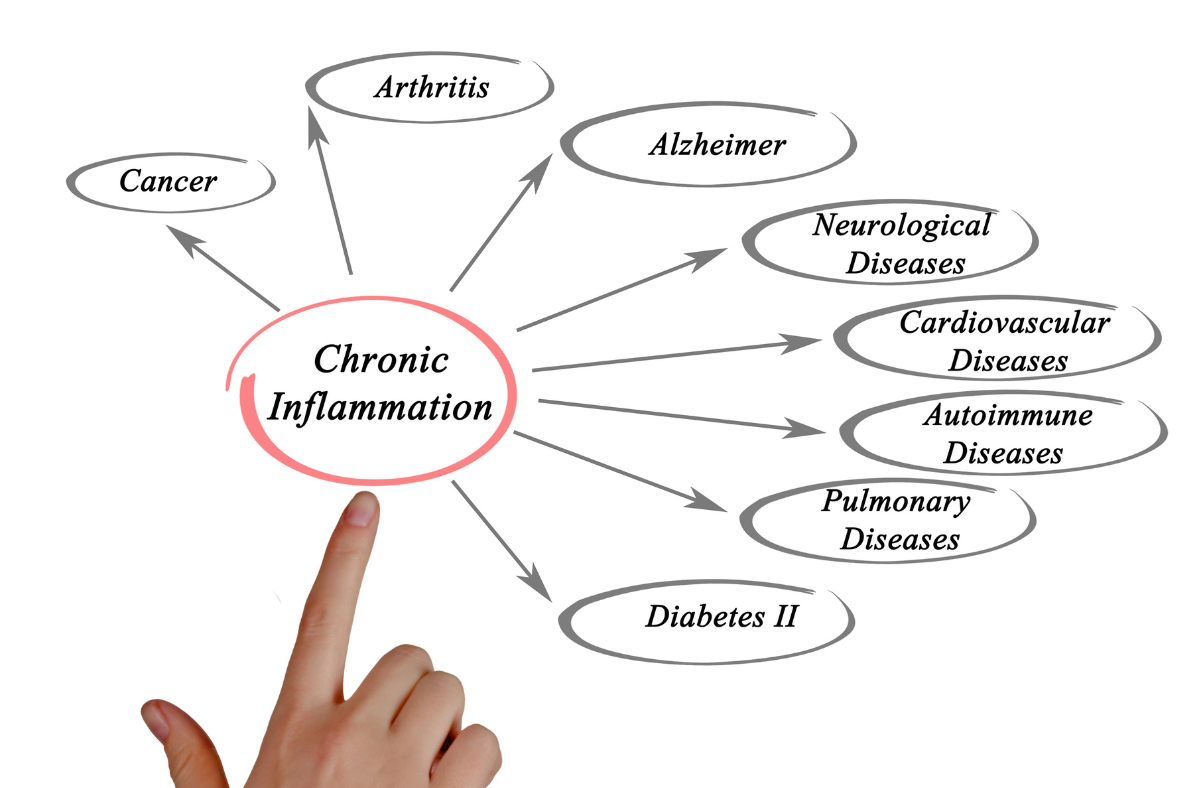
Chronic inflammation occurs when the immune system is continuously activated, leading to the release of inflammatory molecules such as cytokines and chemokines. This can cause damage to tissues and organs over time, leading to a range of health problems.
One of the main consequences of chronic inflammation is tissue damage. Inflammation can cause oxidative stress, which damages cells and tissues, and can lead to the formation of scar tissue. This can impair the functioning of organs and tissues, leading to chronic diseases such as arthritis, heart disease, and cancer.
Some common causes of inflammation include infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, injuries such as cuts, bruises, or burns, and exposure to irritants such as chemicals or pollutants. Chronic inflammation can also be caused by autoimmune disorders, in which the immune system attacks the body's own tissues.
Symptoms of inflammation can vary depending on the location and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms of inflammation include:
Redness: The affected area may appear red and inflamed.
Heat: The affected area may feel warm to the touch.
Swelling: Inflammation can cause swelling, which can be tender or painful.
Pain: Inflammation can cause pain, which can range from mild to severe.
Loss of function: Inflammation can sometimes limit the movement or function of the affected area.
In addition to these common symptoms, inflammation can also cause other symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and headaches. If you are experiencing symptoms of inflammation, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Inflammation can also affect the functioning of the immune system itself. Chronic inflammation can lead to the suppression of the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections and diseases.
Finally, chronic inflammation can also contribute to the development of insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels and an increased risk of diabetes.
Overall, while inflammation is a necessary process for the immune system, chronic inflammation can have damaging effects on the body, leading to a range of chronic diseases and health problems.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 










Write A Comment